Management Tools
Supply Chain Management synchronizes the efforts of all parties—suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, dealers, customers and so on—involved in meeting a customer’s needs. The approach often relies on technology to enable seamless exchanges of information, goods and services across organizational boundaries. It forges much closer relationships among all links in the value chain in order to deliver the right products to the right places at the right times for the right costs. The goal is to establish such strong bonds of communication and trust among all parties that they can effectively function as one unit, fully aligned to streamline business processes and achieve total customer satisfaction.
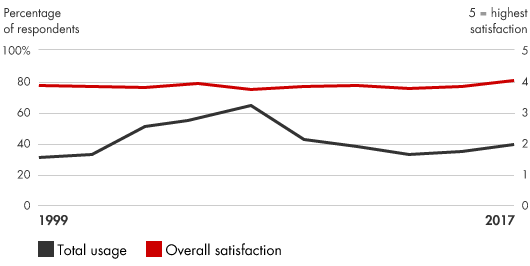
Usage and satisfaction among survey respondents
How Supply Chain Management works:
Companies typically implement Supply Chain Management in four stages:
- Stage One seeks to increase the level of trust among vital links in the supply chain. Managers learn to treat former adversaries as valuable partners. This stage often leads to longer commitments with preferred partners.
- Stage Two increases the exchange of information. It creates more accurate, up-to-date knowledge of demand forecasts, inventory levels, capacity utilization, production schedules, delivery dates and other data that could help supply chain partners improve performance.
- Stage Three expands efforts to manage the supply chain as one overall process rather than dozens of independent functions. It leverages the core competencies of each player, automates information exchange, changes management processes and incentive systems, eliminates unproductive activities, improves forecasting, reduces inventory levels, cuts cycle times and involves customers more deeply in the Supply Chain Management process.
- Stage Four identifies and implements radical ideas to transform the supply chain completely and deliver customer value in unprecedented ways.
| RELATED TOPICS | HOW BAIN CAN HELP |
|---|---|
|
Companies use Supply Chain Management to:
Recognizing that value is leaking out of the supply chain, but that only limited improvement can be achieved by any single company, managers turn to Supply Chain Management to help them deliver products and services faster, better and less expensively.
Supply Chain Management capitalizes on many trends that have changed worldwide business practices, including just-in-time (JIT) inventories, electronic data interchange (EDI), outsourcing of noncore activities, supplier consolidation and globalization.
Selected references
Ayers, James B. Handbook of Supply Chain Management. 2d ed. Auerbach, 2006.
Fisher, Marshall, and Ananth Raman. The New Science of Retailing: How Analytics Are Transforming the Supply Chain and Improving Performance. Harvard Business Press, 2010.
Frazelle, Edward. Supply Chain Strategy. McGraw-Hill, 2001.
Harvard Business Review on Supply Chain Management. Harvard Business School Press, 2006.
Hugos, Michael H. Essentials of Supply Chain Management. 3d ed. Wiley, 2011.
Martin, James. Lean Six Sigma for Supply Chain Management. 2d ed. McGraw-Hill Professional, 2014.
Narayanan, V.G., and Ananth Raman. “Aligning Incentives in Supply Chains.” Harvard Business Review, November 2004, pp. 94–102, 149.
Slone, Reuben E. “Leading a Supply Chain Turnaround.” Harvard Business Review, October 2004, pp. 114–121.
Slone, Reuben E., J. Paul Dittmann, and John T. Mentzer. New Supply Chain Agenda: The 5 Steps That Drive Real Value. Harvard Business Review Press, 2010.
Trent, Robert J. Strategic Supply Management: Creating the Next Source of Competitive Advantage. J. Ross Publishing, 2007.